PostgreSQL – JSON_AGG Function
The json_agg function is used to aggregate values into a JSON array in PostgreSQL database. It takes one or more values and returns a JSON array that contains those values as elements. This function is particularly useful when you want to combine rows or values into a single JSON array in the result of a query.
Here is the basic syntax for the json_agg function:
json_agg(expression)where expression is the value or column you want to aggregate into the JSON array.
Here’s an example of how to use the json_agg function to aggregate values from a table:
Consider a table named employees:
CREATE TABLE employees ( id serial PRIMARY KEY, name text, department text );And it contains the following data:
| id | name | department ||----|--------|------------|| 1 | Alice | HR || 2 | Bob | IT || 3 | Carol | HR || 4 | David | IT |
You can use the json_agg function to aggregate the names of employees in the “HR” department into a JSON array:
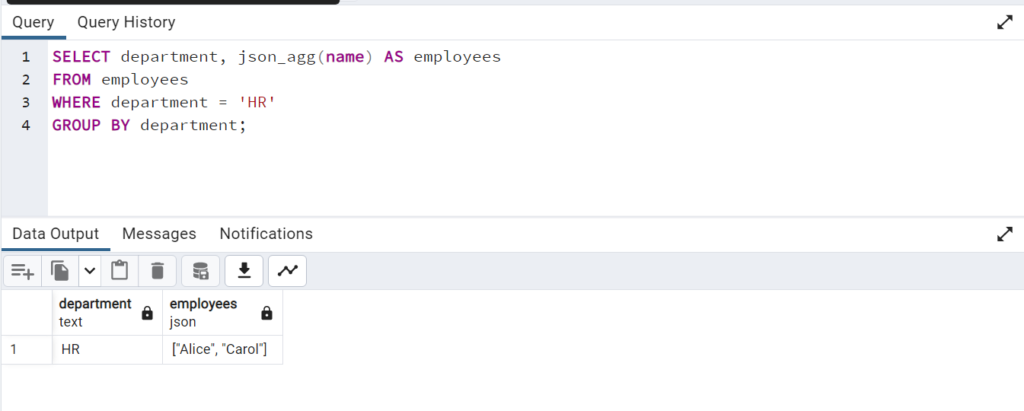
SELECT department, json_agg(name) AS employeesFROM employeesWHERE department = 'HR'GROUP BY department;
The result of this query will be:
| department | employees ||------------|------------------|| HR | ["Alice", "Carol"] |
In this example:
- We selected the department and used
json_agg(name)to aggregate the names of employees in the “HR” department into a JSON array. - The
GROUP BYclause groups the results by department.
The json_agg function is useful for creating JSON arrays from query results, which can be particularly handy when working with JSON data in PostgreSQL.