PostgreSQL – How to Generate a Random Number within a Range
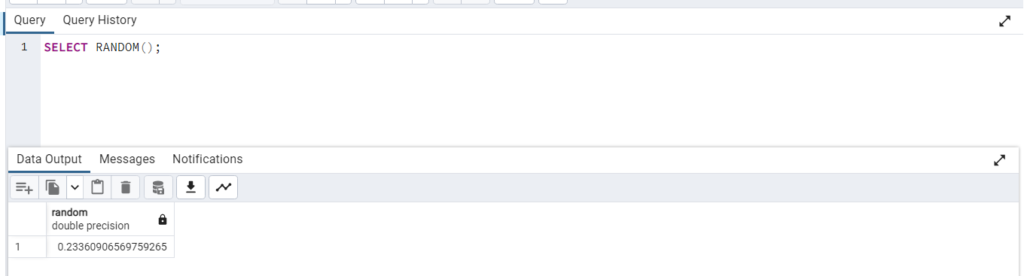
You can use the RANDOM() function to generate a random floating-point number between 0 and 1 in PostgreSQL database. Here’s the basic syntax for using the RANDOM() function:
SELECT RANDOM();
This will return a random number in the range [0, 1), meaning it can be any decimal value between 0 (inclusive) and 1 (exclusive).
If you want to generate random integers within a specific range, you can use the following formula:
SELECT floor(random() * (max - min + 1) + min);
Here
random()generates a random floating-point number in the range [0, 1).(max - min + 1)represents the range of integers you want.floor()is used to round down the floating-point number to the nearest integer.minis the lower bound of the range, andmaxis the upper bound.
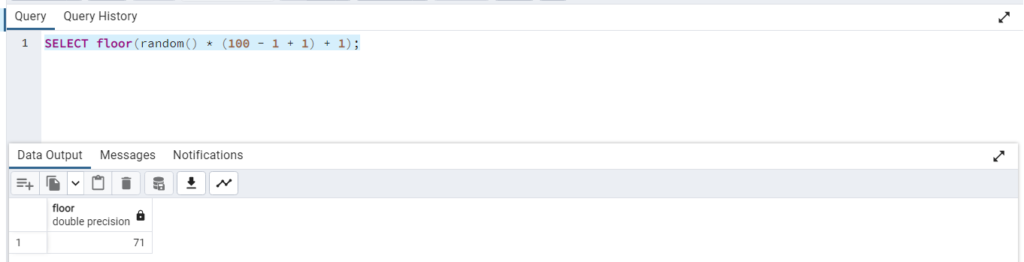
For example, if you want to generate a random integer between 1 and 100 (inclusive), you can use the following SQL query:
SELECT floor(random() * (100 - 1 + 1) + 1);
This will give you a random integer between 1 and 100.