PostgreSQL – Insert into Table
To insert data into a table in PostgreSQL, you can use the INSERT statement. Below is the syntax:
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3, ...) VALUES (value1, value2, value3, ...);
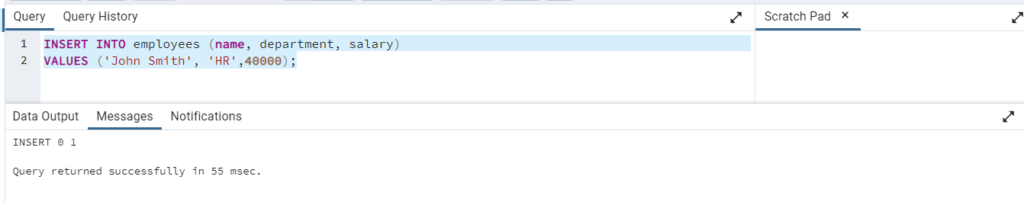
Below is an example of inserting data into a table named “employees” with columns “id”, “name”, and “age”:
INSERT INTO employees (name, department, salary)
VALUES ('John Smith', 'HR',40000);
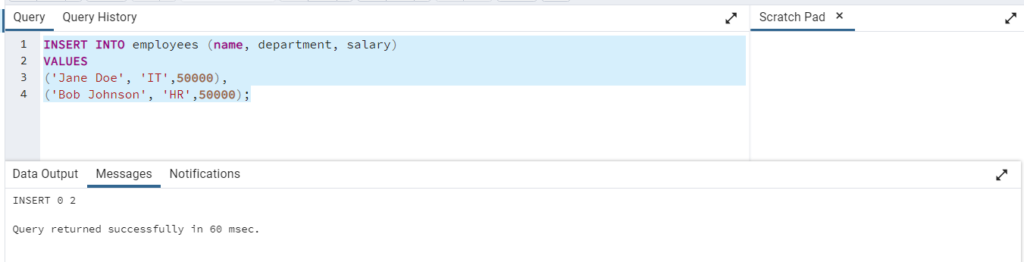
You can also insert multiple rows at once by providing multiple sets of values separated by commas. Here is the syntax to insert multiple rows at once:
INSERT INTO employees (name, department, salary)
VALUES
('Jane Doe', 'IT',50000),
('Bob Johnson', 'HR',50000);
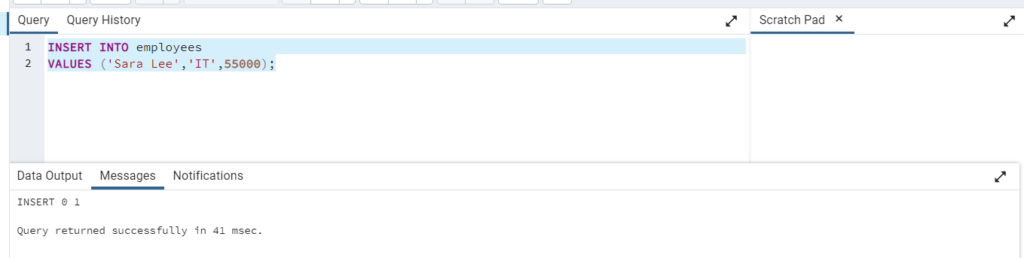
You can omit the column list if you have data to insert into all columns of a table.
INSERT INTO employeesVALUES (4, 'Sara Lee', 31);
The order of the values in the VALUES clause must match the order of the columns in the table definition. If you don’t specify a value for a column that doesn’t allow NULL values, PostgreSQL will throw an error. For nullable columns, you must specify NULL in the values clause.